What are AI application security solutions?
While traditional cybersecurity solutions wont work on AI Applications due to the differences between AI and traditional software, many of the techniques and best practices can be reappropriated at each stage of the AI development lifecycle.
Securing AI Application Development
Like the traditional software supply chain, the AI supply chain includes software dependencies from the initial stages of development. But it also often involves third-party training data and model components, such as open-domain models from repositories like Hugging Face. It is critical that these models be scanned for unsafe or malicious code in the file formats, as well as for unsafe or insecure behaviors of the model to be used in an application.
Whether using open-domain, commercial models or proprietary models, it is necessary to validate the model for potential security and safety issues. For example, fine-tuning a well-aligned foundation model can destroy alignment in ways that must be understood by the application developer. Model validation consists of testing a models susceptibility to the universe of inputs that can elicit unsafe or insecure outcomes. The only requirement is API-or black box-access to a model. This process should be repeated every time there are changes to a model.
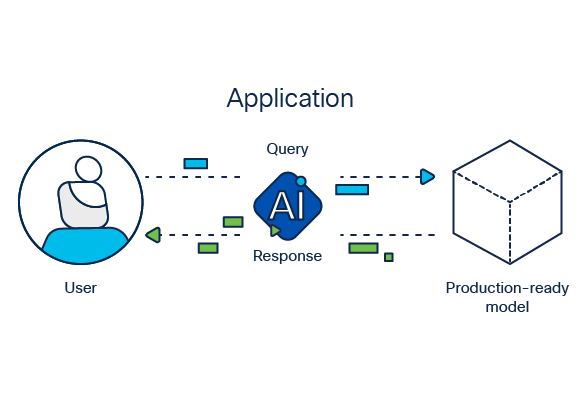
Securing AI application deployment
Once an AI application is put into production, it’s important to continually scan the AI application for emerging safety and security vulnerabilities. These vulnerability scans should be informed by ongoing threat intelligence to ensure that the application is not susceptible to new attacker techniques.
Unlike traditional software vulnerabilities, AI vulnerabilities cannot be patched, so they must be controlled. An AI application firewall enables AI application developers to block malicious requests and undesired information from reaching the model, as well as unsafe responses from reaching the end-user. Resulting logs can be passed to a security ticketing system and a security information and event management (SIEM) solution to be evaluated as part of the companys preferred security workflow.